Megajadi.com – Formaldehyde, Formaldehyde Services
Can Formaldehyde Be Cured?
Formaldehyde is a colorless, flammable gas often found in various household products, construction materials, and industrial applications. While it plays a significant role in manufacturing and preservation, formaldehyde exposure has raised health concerns due to its potential adverse effects on humans. But the question remains: can formaldehyde be “cured” or neutralized? Let’s dive into the science and practical solutions.
Understanding Formaldehyde
Formaldehyde is commonly used in:
- Adhesives and bonding agents in furniture and construction materials.
- Preservatives in medical laboratories and cosmetics.
- Disinfectants and industrial processes.
While its applications are widespread, prolonged exposure to formaldehyde can irritate the eyes, nose, throat, and skin. In high concentrations, it is classified as a carcinogen, making the mitigation of formaldehyde exposure a critical concern for health and safety.
Can Formaldehyde Be Cured?
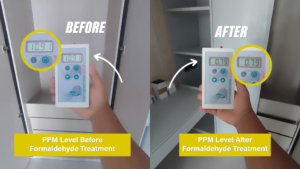
The term “cure” can be misleading. While formaldehyde cannot be entirely eliminated from materials once integrated, its effects can be minimized or neutralized through specific methods. Below are practical approaches:
1. Ventilation and Air Purification
- Ventilation: Regularly circulating fresh air reduces formaldehyde concentrations indoors. Open windows and use exhaust fans, especially in spaces with new furniture or construction.
- Air Purifiers: Devices with activated carbon filters can capture and neutralize formaldehyde particles in the air.
2. Chemical Neutralizers
Certain chemical treatments can break down formaldehyde into less harmful compounds:
- Ammonia-Based Solutions: These can react with formaldehyde to form hexamethylenetetramine, a stable compound. However, professional guidance is necessary to avoid secondary risks.
- Potassium Permanganate: Often used in industrial settings, this can oxidize formaldehyde into safer substances.
3. Absorbent Materials
Natural absorbents like bamboo charcoal and zeolite are known for their ability to trap formaldehyde molecules. These materials are affordable and can be placed around affected areas for continuous absorption.
4. Time and Natural Dissipation
Formaldehyde emissions decrease over time as materials off-gas. However, this process can take years, depending on the concentration and type of material. Regular cleaning and maintenance can accelerate this dissipation.
Preventative Measures
The best way to “cure” formaldehyde-related issues is to minimize its introduction in the first place:
- Choose Low-Formaldehyde Products: Look for items labeled as “formaldehyde-free” or compliant with safety standards like CARB Phase 2 or E1.
- Seal Surfaces: Applying a sealant to materials like plywood and MDF can limit formaldehyde emissions.
- Maintain Proper Humidity Levels: High humidity can increase formaldehyde release. Using dehumidifiers helps mitigate this effect.
Conclusion
While formaldehyde cannot be entirely “cured” in the sense of being removed from materials, its effects can be managed and mitigated effectively. By employing ventilation, air purification, chemical neutralizers, and preventative strategies, individuals can reduce exposure and maintain healthier indoor environments. Awareness and proactive measures are the keys to minimizing the risks associated with formaldehyde.
Remember, a safer home or workspace begins with informed decisions and consistent efforts to improve air quality.
Is Your Home Safe? Book Your Formaldehyde Test Today!